How Does it Work?
Powder defoamers work through a multi-faceted approach that disrupts the formation and stability of foam.
- Dispersion: The powder defoamer, typically composed of ingredients like polyols, polysiloxanes, polyglycols, or vegetable/mineral oils, readily disperses throughout the mortar mix.
- Interface Activity: The defoamer components migrate to the air-liquid interface of the bubbles.
- Foam Film Destabilization: The defoamer weakens the surface tension of the bubble film, making it unstable and prone to rupture. Imagine a soap bubble popping when touched; the defoamer acts in a similar way, weakening the bubble structure.
- Bubble Coalescence: The ruptured bubbles coalesce, forming larger bubbles that readily rise to the surface and dissipate.
- Prevention of Re-Entrainment: By continually disrupting the foam structure, the defoamer prevents the re-entrainment of air during mixing and application.
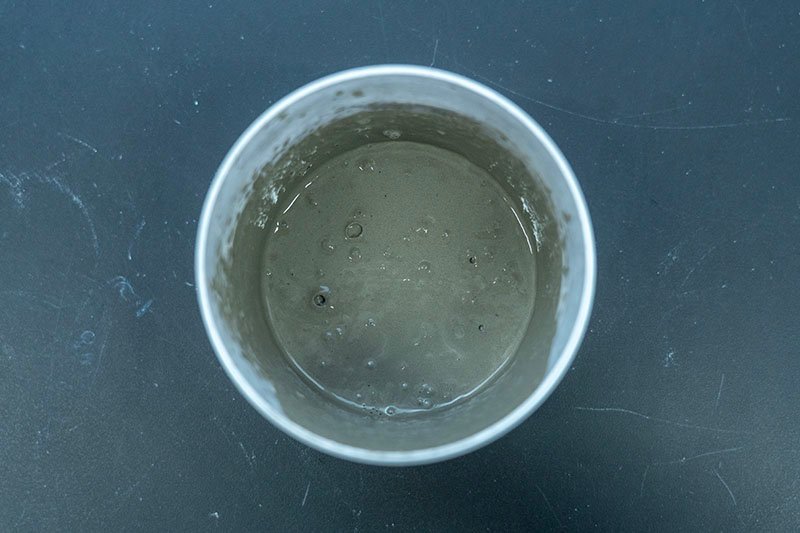
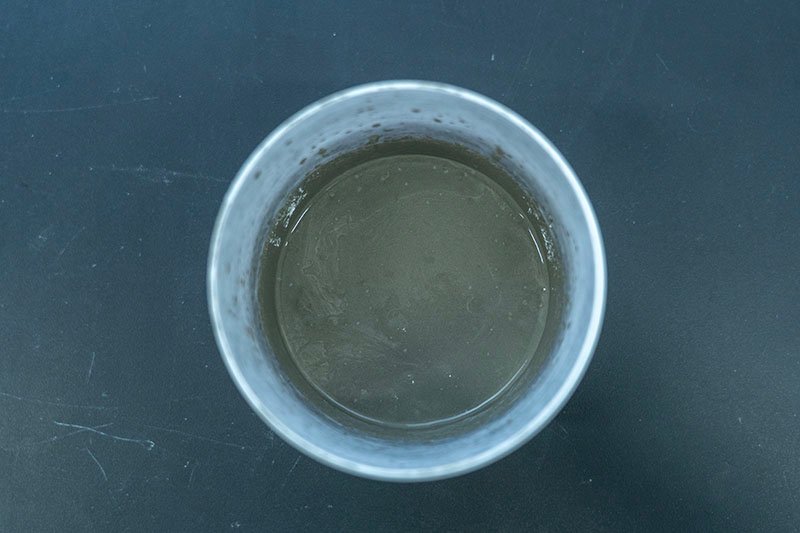
The result is a significant reduction in air content, leading to a more homogenous and dense grout. This, in turn, translates to superior performance characteristics. Powder defoamers, such as those based on polyols, polysiloxanes, polyglycols, and vegetable or mineral oils, work by dispersing in the mortar and quickly collapsing foam bubbles created during mixing.